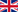
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a fundamental protocol used in local area networks (LAN) to convert an IP address into a physical address, typically a MAC address. It operates at the link layer of the OSI model and plays a crucial role in ensuring that data packets are sent to the correct destination within a local network.
How ARP Works?
- ARP Request: When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same local network, it first checks its ARP cache to see if it already knows the MAC address of the destination IP. If not, it broadcasts an ARP request to all devices on the network.
- ARP Reply: The device with the matching IP address responds with an ARP reply, revealing its MAC address.
- Cache Update: The requesting device updates its ARP cache with the new information to avoid future broadcasts for the same IP.
ARP Table
Every device on a local network maintains an ARP table, a cache of IP-to-MAC address mappings. This table is consulted before any ARP request is broadcasted, optimizing network traffic.
Types of ARP Messages
- ARP Request: A broadcast message asking "Who has this IP address?"
- ARP Reply: A direct response to the requester with the MAC address.
- RARP (Reverse ARP): Used to obtain an IP address using a MAC address.
- Gratuitous ARP: A device announces its IP and MAC address to the entire network, often used to detect IP conflicts.
Security Concerns with ARP
- ARP doesn't have built-in security features, leading to potential vulnerabilities:
- ARP Spoofing/Poisoning: A malicious device can send fake ARP messages to associate its MAC address with the IP address of another device.
- ARP Cache Poisoning: A malicious device can send unsolicited ARP replies to update other devices' ARP caches with incorrect mappings.
Mitigating ARP Threats
- Static ARP: Manually set IP-to-MAC address mappings.
- ARP Inspection: Network switches can inspect ARP packets to prevent spoofing.
- VPN & Encryption: Encrypting traffic can prevent man-in-the-middle attacks resulting from ARP spoofing.
Conclusion
ARP is a foundational protocol for local network communication. While it's simple and efficient, it's essential to be aware of its vulnerabilities and take measures to ensure network security.
While our company name "ARP Ideas" might evoke thoughts of the Address Resolution Protocol, a foundational element in networking, our expertise lies elsewhere. We're well-acquainted with the ARP technology, but it's not the main service we offer. Instead, our strengths are channeled into a diverse range of digital solutions and services that drive business transformations. We invite you to explore our website to discover the innovative services we're proud to provide to our clients.